The Intersection of Data and Cybersecurity

Future of DevOps: Trends and Techniques
Education is the cornerstone of social progress, which shapes the minds and talents of the next generation. As the world is getting rapidly digital, data has emerged as a transformative force in education which provides unprecedented opportunities to enhance educational institutions teaching, learning and management. With the power of data analytics, individual learning, and informed decision -making, education system worldwide is becoming more effective, justified and adaptive.
Further, in this newsletter, we will explore the important role of data in education, how it is empowering students, teachers and administrators, and data-driven educational landscape challenges and future possibilities.
The Rise of Data in Education
Integration of data with education - which is often referred to as educational data or learning analytics - has gained momentum due to digital learning tools, online assessment and expansion of student information systems. These sources generate large amounts of data by incorporating students' performance, behavior, engagement and course effectiveness.
Educational data enables schools, colleges and universities to move to evidence-based decisions from intuition-based decisions, optimizing learning processes and institutional results.
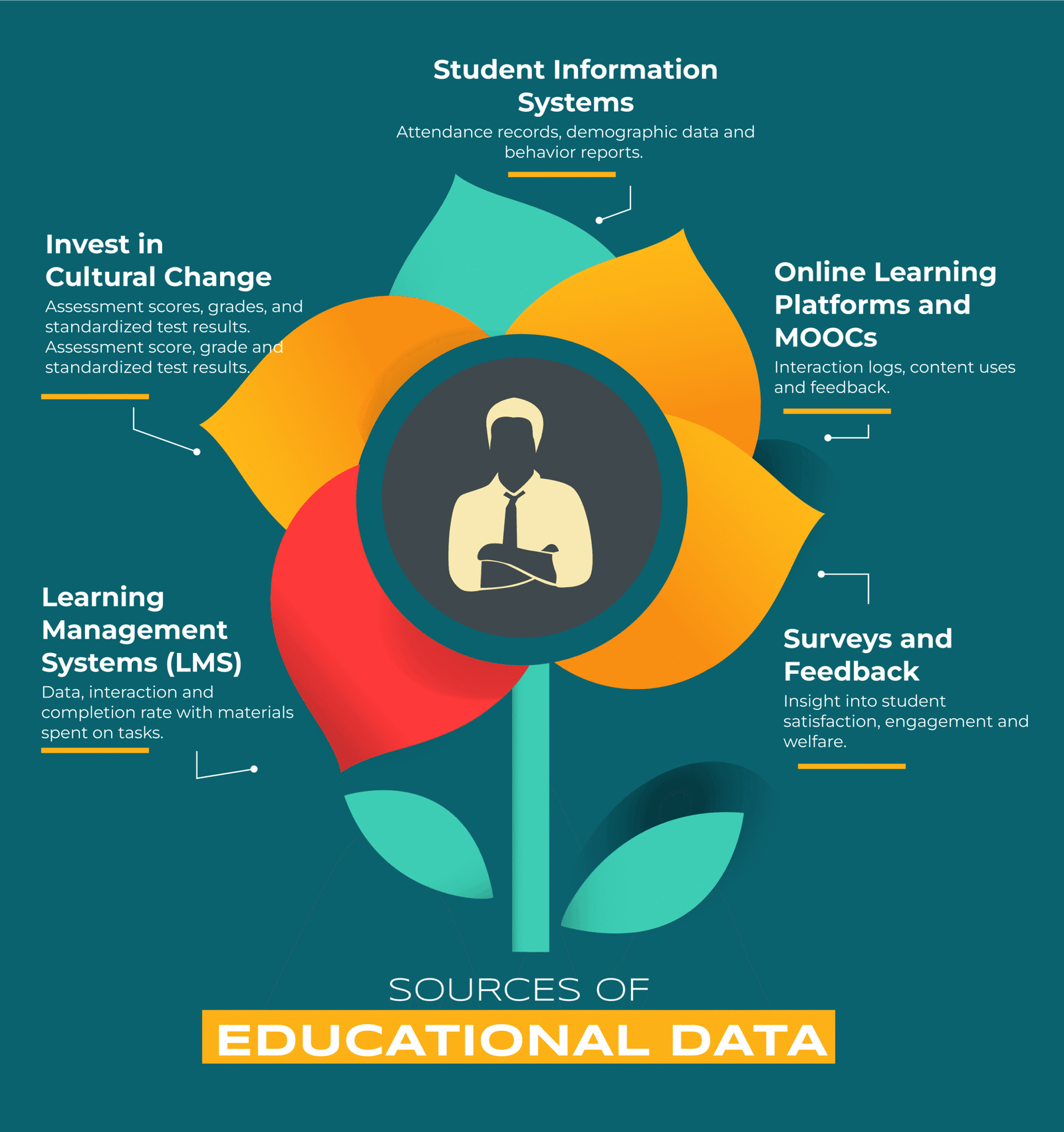
Sources of Educational Data
- Student Performance Data: Assessment scores, grades, and standardized test results. Assessment score, grade and standardized test results.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Data, interaction and completion rate with materials spent on tasks.
- Student Information Systems: Attendance records, demographic data and behavior reports.
- Online Learning Platforms and MOOCs: Interaction logs, content uses and feedback.
- Surveys and Feedback: Insight into student satisfaction, engagement and welfare.
Sources of Educational Data
How Data Empowers Students
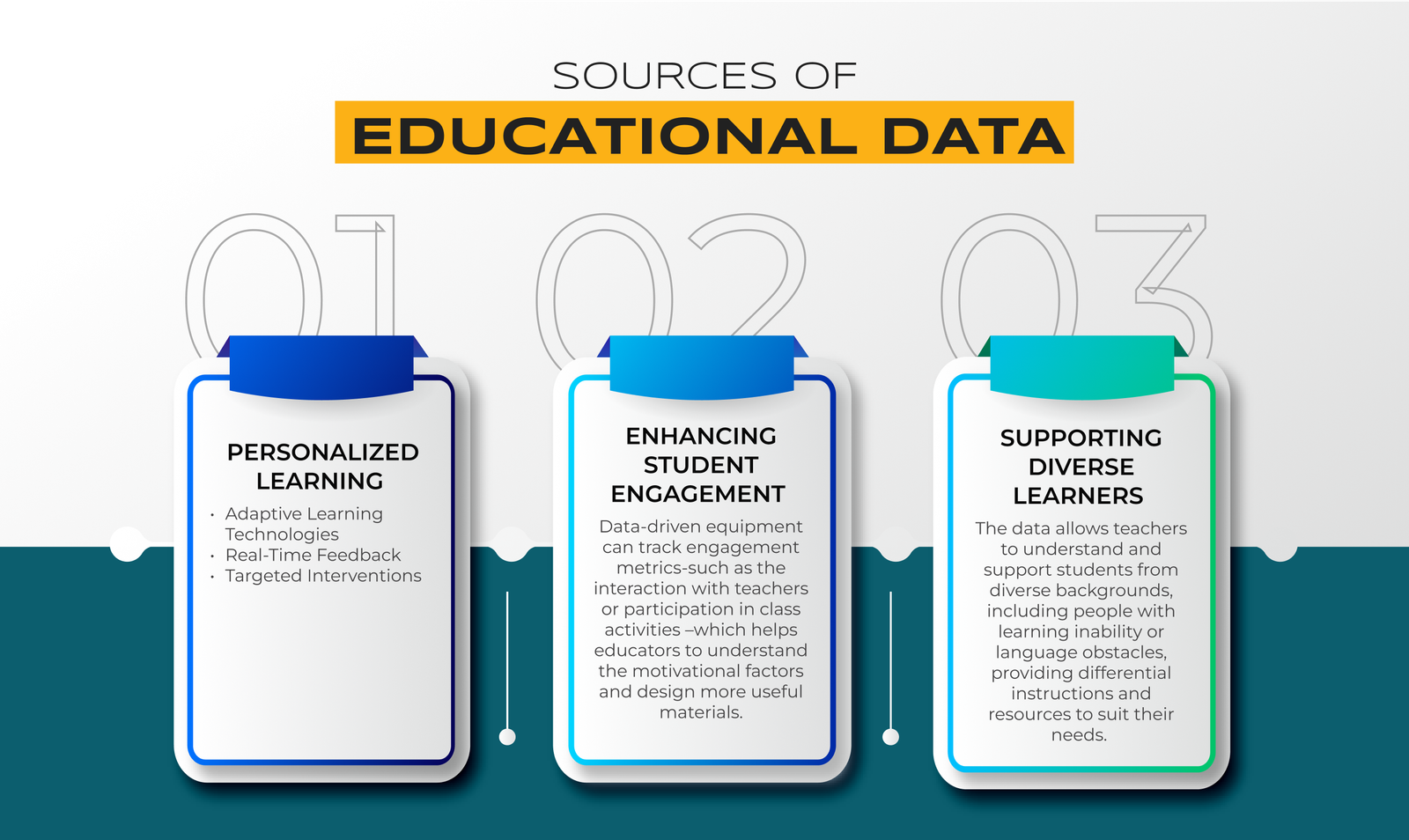
Personalized Learning
One of the most powerful applications of data in education lies in personalizing learning experiences to meet the unique needs of each student. Teachers can customize instructions and materials by analyzing data on the students' strength, weaknesses and learning styles.
- Adaptive Learning Technologies: Students use data to adjust the level of platform difficulty, suggest resources and create individual learning paths.
- Real-Time Feedback: Data analytics provide immediate insights into their progress, motivating improvement and self-directed learning.
- Targeted Interventions: The initial warning system identifies struggling students, capable of timely support to prevent dropouts.
Enhancing Student Engagement
Data-driven equipment can track engagement metrics-such as the interaction with teachers or participation in class activities –which helps educators to understand the motivational factors and design more useful materials.
Supporting Diverse Learners
The data allows teachers to understand and support students from diverse backgrounds, including people with learning inability or language obstacles, providing differential instructions and resources to suit their needs.
How Data Empowers Students
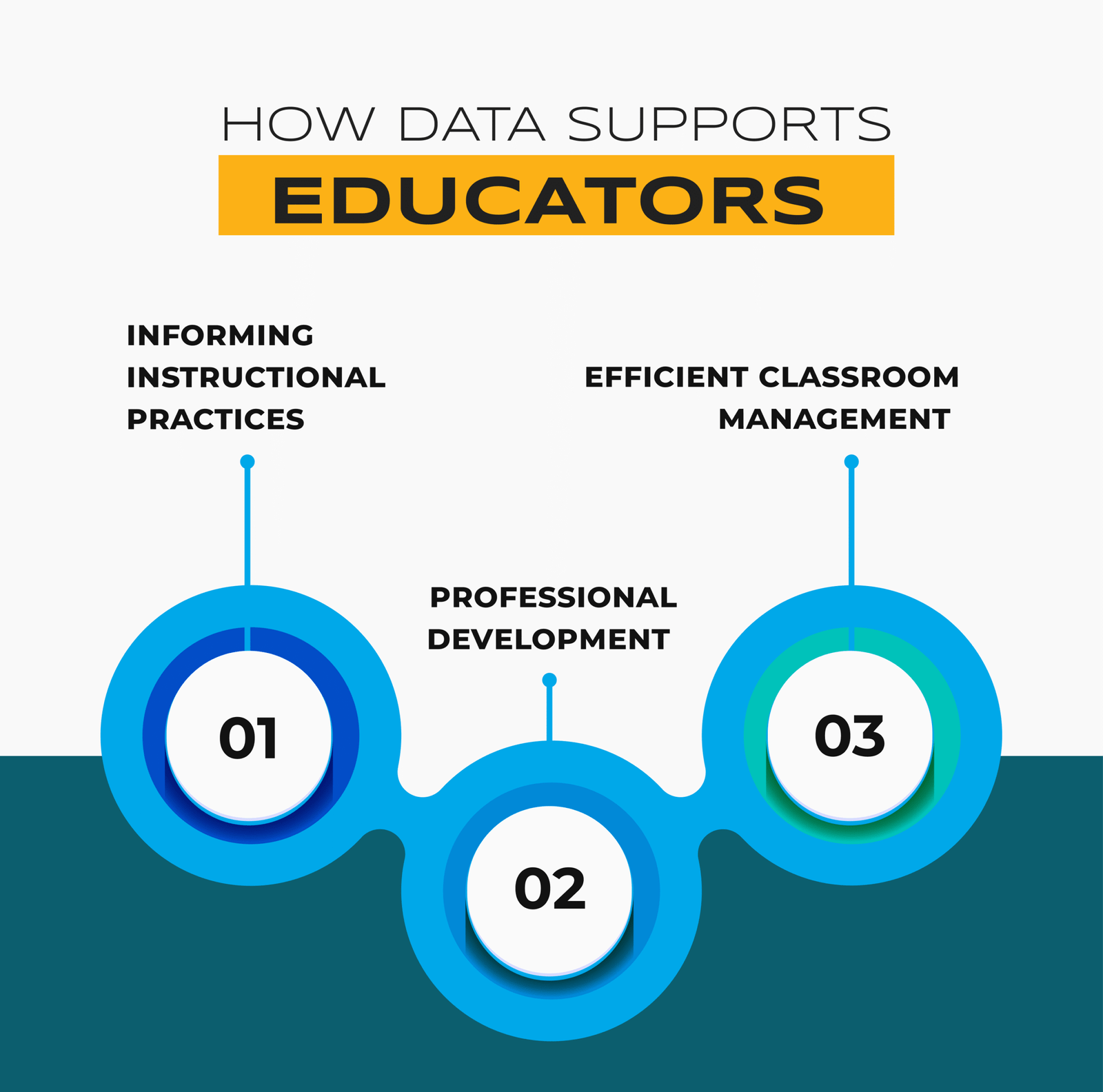
How Data Supports Educators
- Informing Instructional Practices
Teachers can avail data analytics to identify which teaching strategies are working and which areas require improvement. This evidence-based approach leads to more effective lesson planning and class management.
- Professional Development
Data can expose gaps in teacher knowledge or practices. Hence, it guides targeted training programs and professional development initiatives.
- Efficient Classroom Management
By monitoring appearance, behavior and engagement figures, teachers can identify trends and challenges in the classroom, allowing active strategies to promote a positive learning environment.
How Data Supports Educators
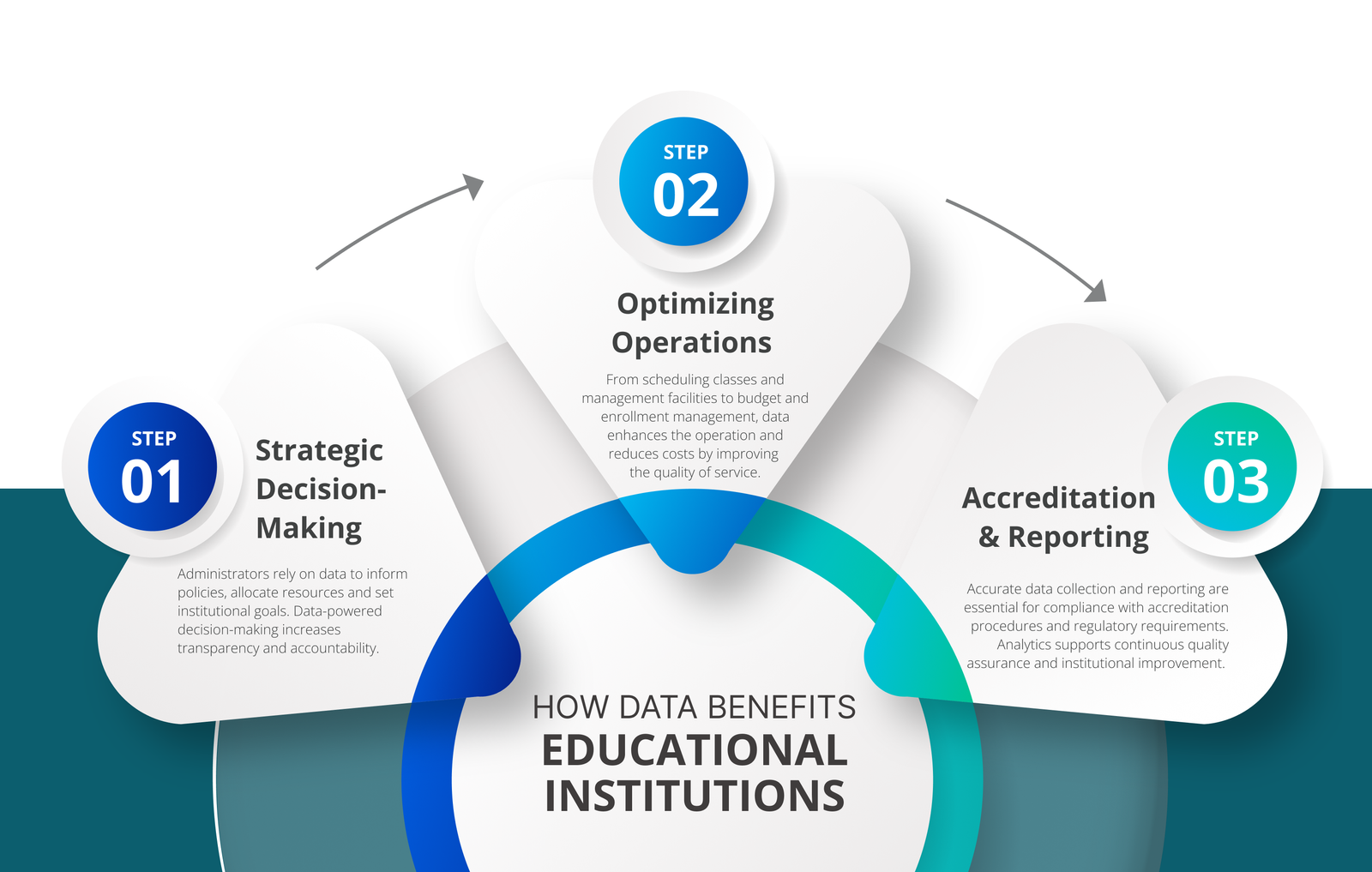
How Data Benefits Educational Institutions
- Strategic Decision-Making
Administrators rely on data to inform policies, allocate resources and set institutional goals. Data-powered decision-making increases transparency and accountability.
- Optimizing Operations
From scheduling classes and management facilities to budget and enrollment management, data enhances the operation and reduces costs by improving the quality of service.
- Accreditation and Reporting
Accurate data collection and reporting are essential for compliance with accreditation procedures and regulatory requirements. Analytics supports continuous quality assurance and institutional improvement.
How Data Benefits Educational Institutions
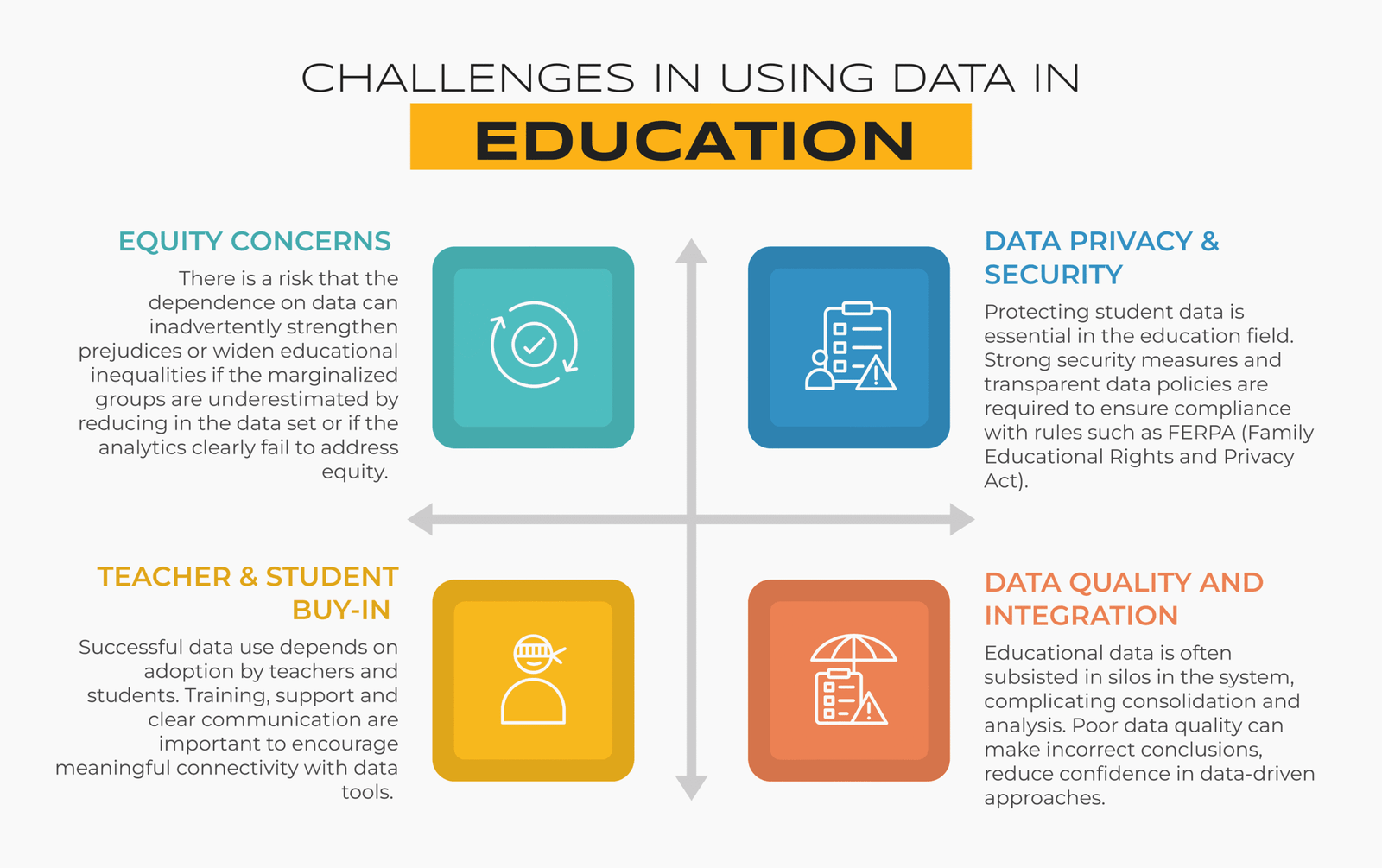
Challenges in Using Data in Education
- Data Privacy and Security
Protecting student data is essential in the education field. Strong security measures and transparent data policies are required to ensure compliance with rules such as FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act).
- Data Quality and Integration
Educational data is often subsisted in silos in the system, complicating consolidation and analysis. Poor data quality can make incorrect conclusions, reduce confidence in data-driven approaches.
- Equity Concerns
There is a risk that the dependence on data can inadvertently strengthen prejudices or widen educational inequalities if the marginalized groups are underestimated by reducing in the data set or if the analytics clearly fail to address equity.
- Teacher and Student Buy-In
Successful data use depends on adoption by teachers and students. Training, support and clear communication are important to encourage meaningful connectivity with data tools.
Challenges in Using Data in Education
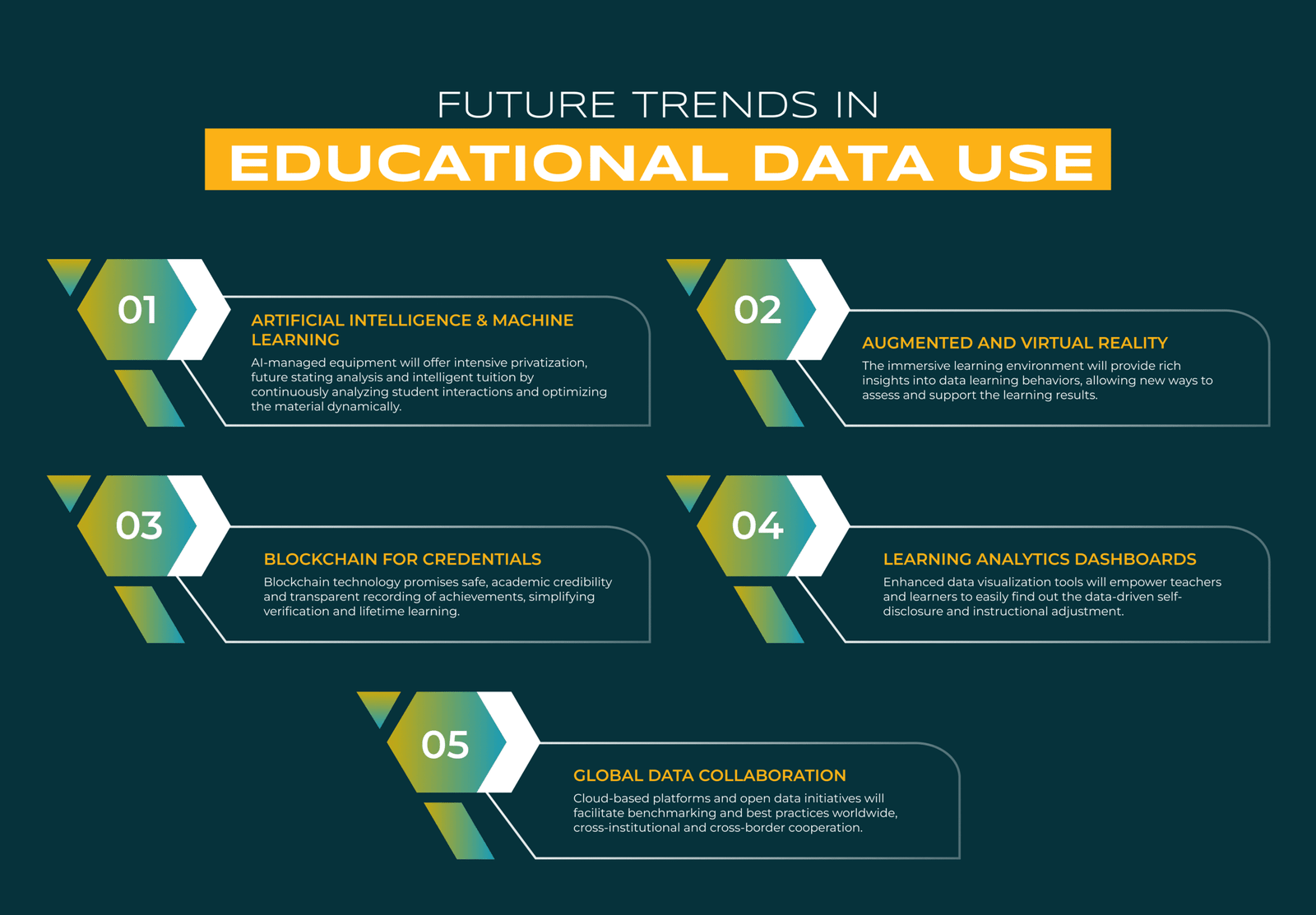
Future Trends in Educational Data Use
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-managed equipment will offer intensive privatization, future stating analysis and intelligent tuition by continuously analyzing student interactions and optimizing the material dynamically.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality
The immersive learning environment will provide rich insights into data learning behaviors, allowing new ways to assess and support the learning results.
- Blockchain for Credentials
Blockchain technology promises safe, academic credibility and transparent recording of achievements, simplifying verification and lifetime learning.
- Learning Analytics Dashboards
Enhanced data visualization tools will empower teachers and learners to easily find out the data-driven self-disclosure and instructional adjustment.
- Global Data Collaboration
Cloud-based platforms and open data initiatives will facilitate benchmarking and best practices worldwide, cross-institutional and cross-border cooperation.
Future Trends in Educational Data Use
Case-Studies: Real Life Use of Data in Education
Case Study 1: Arizona State University’s Adaptive Learning Success
Overview:
Arizona State University launched a mission to improve student retention and graduate rates by leveraging data-driven individual teaching technologies. Facing challenges with large, diverse student population and various teaching pace, ASU aims to customize educational experiences for individual students needs.
Implementation:
ASU adopted adaptive teaching platforms that collect and analyze real -time student performance data in many courses. These platforms dynamically accommodate material difficulty, provide personal resources, and provide target response to students. Teachers used data dashboard collected to monitor progress and intervene when necessary.
Results:
- ASU saw a significant increase in the rates of student engagement and completion of the course.
- Retention rates increased by more than 10% in programs using adaptive teaching technologies.
- The faculty reported better insight into the needs of individual students, enabling more targeted teaching strategies.
- Success inspired extended deployment across discipline, promoting the culture of continuous data-informed improvement.
Lessons Learned:
- Personal learning by data, increases student motivation and academic performance.
- Continuous data monitoring allows timely intervention that can reduce the dropout risk.
- Institutional commitment and faculty training are important in effectively integrating data-driven equipment.
Case Study 2: Chicago Public Schools’ Early Warning System to Reduce Dropouts
Overview:
Chicago Public Schools demanded high dropout rates and demanded a systemic approach to identify at risk students as early as possible to provide support and improve results.
Implementation:
CPS applied a predictive analytics-driven initial warning system, leveraging attendance, grade, behavior and other demographic data. The system generates risk scores for each student, which reduces the possibility of leaving or failing those people. Teachers and consultants received actionable alerts, enabling targeted intervention such as tutoring, mentoring or counseling services.
Results:
- CPS reduced the dropout rates of about 20%in participating schools.
- Timely support for at-risk students improved attendance and educational performance.
- The data-driven approach improved resource allocation, enabled schools to focus on those efforts where the most influential.
- Success helped CPS secure additional funding to expand the district-wide system.
Lessons Learned:
- The initial identity of struggling students is important to prevent dropouts and improve educational success.
- Cross-functional cooperation between data analysts, teachers and counselors ensures effective intervention strategies.
- Data transparency and ongoing staff training foster trust and increase system benefits.
Conclusion
These case studies throw light on the fact that data-managed practices in education-ranging from individual teaching platforms to forecasting risk models-are changing the results and strengthening the next generation with conforming support and opportunities.
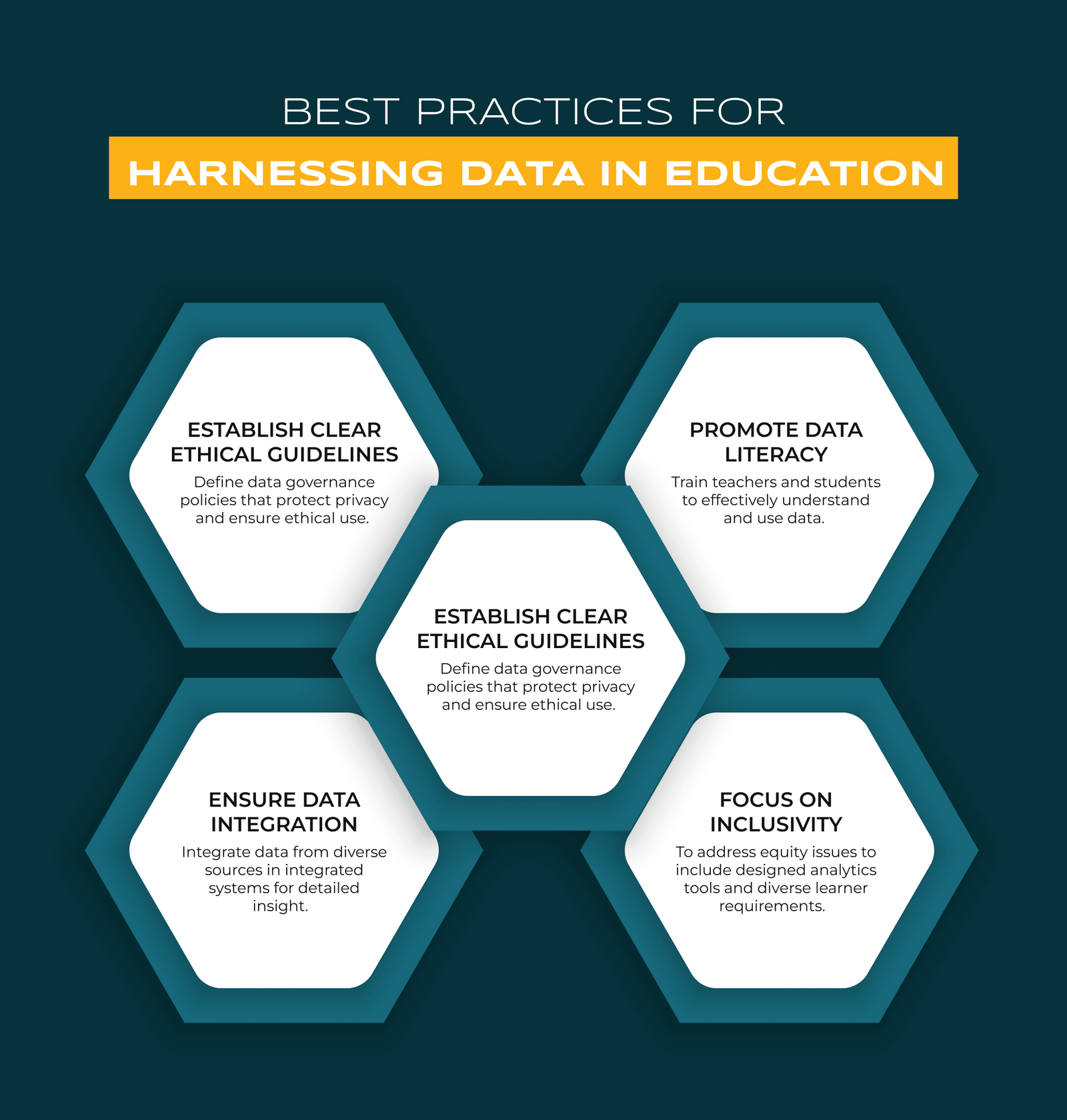
Best Practices for Harnessing Data in Education
- Establish Clear Ethical Guidelines: Define data governance policies that protect privacy and ensure ethical use.
- Promote Data Literacy: Train teachers and students to effectively understand and use data.
- Ensure Data Integration: Integrate data from diverse sources in integrated systems for detailed insight.
- Focus on Inclusivity: To address equity issues to include designed analytics tools and diverse learner requirements.
- Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement: Use data as a feedback mechanism to adapt and enhance continuous optimization teaching and learning.
Best Practices for Harnessing Data in Education
Wrapping Up
Data is bringing revolution in education by strengthening students, teachers and institutions to make informed decisions and customize learning experiences. As the future comes near, data-driven education promises more individual, skilled and equitable systems that prepare the next generation for challenges and opportunities.
To fully utilize the ability of the data, the education field requires conscious efforts to ensure privacy, quality and inclusion. With thoughtful implementation and ongoing innovation, data will remain a powerful tool in unlocking human ability and shaping the future of education.
As educators and stakeholders embrace this change, the collective effect will be deeper - empowering learners everywhere to flourish in a fast complex world.
This Article is also here